The Second Major Wave of Jihad: the Turks, 1071-1683 AD - Islam 101
The complete text on one page (good for printing)
Islam 101 was written by Gregory M. Davis, author of Religion of Peace?: Islam's War Against the World and the producer/director of Islam: What the West Needs to Know .
Islam 101 also appears on JihadWatch: Islam 101 on JW and on Citizen Warrior: Islam 101 on Citizen Warrior
You can view the complete movie online.Jihad and Dhimmitude
What does "jihad" mean?
Muslim Scholar Hasan Al-Banna on jihad
Dar al-Islam and dar al-harb: the House of Islam and the House of War
Taqiyya — Religious Deception
Jihad Through History
The First Major Wave of Jihad: the Arabs, 622-750 AD
The Second Major Wave of Jihad: the Turks, 1071-1683 AD
Some twenty-five years before the first Crusading army set out from central Europe for the Holy Land, the Turkish (Ottoman) armies began an assault on the Christian Byzantine Empire, which had ruled what is now Turkey since the Roman Empire's capital was moved to Constantinople in 325 AD. At the battle of Manzikert, in 1071, the Christian forces suffered a disastrous defeat, which left much of Anatolia (Turkey) open to invasion. This second wave of jihad was temporarily held up by the invading Latin Armies during the Crusades (see Islam 101 FAQs), but, by the beginning of the 14th century, the Turks were threatening Constantinople and Europe itself.
In the West, Roman Catholic armies were bit by bit forcing Muslim forces down the Iberian peninsula, until, in 1492, they were definitively expelled (the Reconquista). In Eastern Europe, however, Islam continued in the ascendant. One of the most significant engagements between the invading Muslims and the indigenous peoples of the region was the Battle of Kosovo in 1389, where the Turks annihilated a multinational army under the Serbian King, St. Lazar, though their progress into Europe was significantly slowed. After numerous attempts dating back to the seventh century, Constantinople, the jewel of Eastern Christendom, finally fell in 1453 to the armies of Sultan Mahomet II. Lest one ascribe the atrocities of the first wave of jihad to the "Arabness" of its perpetrators, the Turks showed they were fully capable of living up to the principles of the Quran and the Sunnah. Paul Fregosi in his book Jihad describes the scene following the final assault on Constantinople:
- Several thousand of the survivors had taken refuge in the cathedral: nobles, servants, ordinary citizens, their wives and children, priests and nuns. They locked the huge doors, prayed, and waited. {Caliph} Mahomet {II} had given the troops free quarter. They raped, of course, the nuns being the first victims, and slaughtered. At least four thousand were killed before Mahomet stopped the massacre at noon. He ordered a muezzin {one who issues the call to prayer} to climb into the pulpit of St. Sophia and dedicate the building to Allah. It has remained a mosque ever since. Fifty thousand of the inhabitants, more than half the population, were rounded up and taken away as slaves. For months afterward, slaves were the cheapest commodity in the markets of Turkey. Mahomet asked that the body of the dead emperor be brought to him. Some Turkish soldiers found it in a pile of corpses and recognized Constantine {XI} by the golden eagles embroidered on his boots. The sultan ordered his head to be cut off and placed between the horse's legs under the equestrian bronze statue of the emperor Justinian. The head was later embalmed and sent around the chief cities of the Ottoman empire for the delectation of the citizens. Next, Mahomet ordered the Grand Duke Notaras, who had survived, be brought before him, asked him for the names and addresses of all the leading nobles, officials, and citizens, which Notaras gave him. He had them all arrested and decapitated. He sadistically bought from their owners {i.e., Muslim commanders} high-ranking prisoners who had been enslaved, for the pleasure of having them beheaded in front of him. (Fregosi, Jihad, 256-7.)
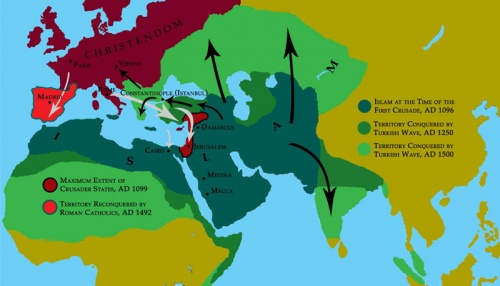
This second, Turkish wave of jihad reached its farthest extent at the failed sieges of Vienna in 1529 and 1683, where in the latter instance the Muslim army under Kara Mustapha was thrown back by the Roman Catholics under the command of the Polish King, John Sobieski. In the decades that followed, the Ottomans were driven back down through the Balkans, though they were never ejected from the European continent entirely. Still, even while the imperial jihad faltered, Muslim land- and sea-borne razzias into Christian territory continued, and Christians were being abducted into slavery from as far away as Ireland into the 19th century.